Surgical Fine-Tuning: Precision Adjustments for Language Models with PyReFT
Surgical Fine-Tuning: Precision Adjustments for Language Models with PyReFT
Fine-tuning large language models (LMs) can be a challenging task, especially when trying to achieve high performance without extensive hardware or time investment. In this post, we explore PyReFT—a reft-native Python library that simplifies and enhances the fine-tuning process. PyReFT introduces a novel approach to fine-tuning that leverages reft-based methodologies, making it easier for developers and researchers to experiment with state-of-the-art language models.
What Is ReFT?
At its core, reft is about rethinking the traditional fine-tuning process by introducing more modular and flexible components into the training pipeline. Rather than applying a one-size-fits-all approach, reft allows users to:
- Customize the fine-tuning steps.
- Integrate novel techniques to adapt to specific datasets or model architectures.
- Optimize the learning process by refining the training loop, which leads to better generalization and faster convergence.
This approach aligns with the ongoing trend in machine learning of creating specialized tools that can be seamlessly integrated into existing pipelines without sacrificing performance.
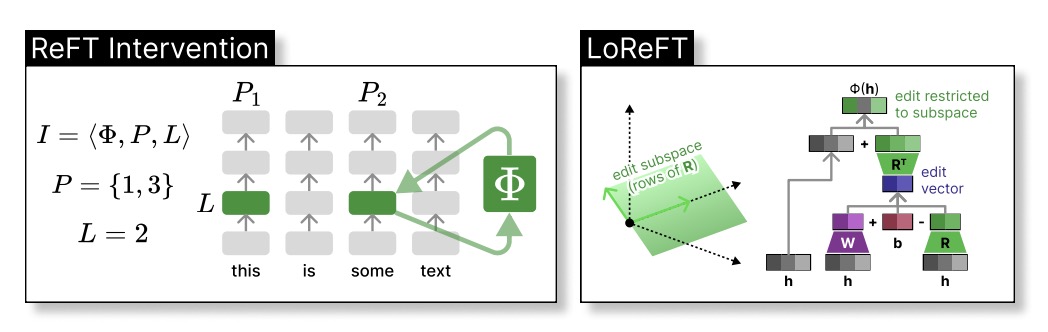
The left panel depicts an intervention I: the intervention function Φ is applied to hidden representations at positions P in layer l. (2) The right panel depicts the intervention function used in LoReFT, which finds an edit vector that only modifies the representation in the linear subspace spanned by the rows of R. Specifically, we show how a rank-2 LoReFT operates on 3-dimensional hidden representations.
Source: ReFT: Representation Finetuning for Language Models
Why PyReFT?
PyReFT was developed to address some of the key challenges in fine-tuning:
- Ease of Use: The library is designed with a clean API that allows users to quickly set up experiments without having to write boilerplate code.
- Flexibility: Whether you’re working with transformer-based models or other architectures, PyReFT provides a modular framework that you can extend or modify as needed.
- Performance: By adopting a reft-native approach, the library enables more efficient use of computational resources, leading to faster training times and improved model performance.
Overview of the Library
PyReFT brings several innovative features to the table:
Modular Configuration: The library uses configuration objects to encapsulate model parameters, datasets, and training hyperparameters. This makes it straightforward to run multiple experiments with minimal changes.
Enhanced Training Loop: The fine-tuning process in PyReFT is designed to incorporate dynamic adjustments. This might include adaptive learning rate schedules, gradient accumulation, or custom loss functions that are better suited for fine-tuning large-scale models.
Seamless Integration: PyReFT works well with popular deep learning frameworks like PyTorch, enabling users to combine its functionalities with existing workflows. Whether you’re prototyping or deploying models in production, the library adapts to your needs.
Example Code
Below is a simple example that demonstrates how to use PyReFT for fine-tuning a language model. This snippet covers setting up the configuration, initializing the trainer, running the fine-tuning process, and evaluating the model. (The full example will be available on my GitHub repository.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# Import necessary components from PyReFT
import pyreft
from pyreft import ReFConfig, ReFTrainer
# Define a configuration for fine-tuning
config = ReFConfig(
model_name="gpt-neo", # Model to fine-tune
dataset_name="wikitext-2", # Dataset for fine-tuning
learning_rate=3e-5, # Learning rate for the optimizer
epochs=3, # Number of fine-tuning epochs
batch_size=16 # Batch size for training
)
# Initialize the trainer with the configuration
trainer = ReFTrainer(config)
# Start the fine-tuning process
trainer.fine_tune()
# Evaluate the fine-tuned model
evaluation_results = trainer.evaluate()
print("Evaluation Results:", evaluation_results)
Code Breakdown
Configuration Setup:
TheReFConfigobject is used to set the model, dataset, and training hyperparameters. This modular approach ensures that you can easily swap out parameters or try different experiments without major changes to the code.Trainer Initialization:
TheReFTrainertakes the configuration and prepares the model and dataset for fine-tuning. It abstracts away the low-level details so that you can focus on experimenting with new ideas.Fine-Tuning & Evaluation:
With a single call tofine_tune(), the library manages the training loop, including any custom reft-based adjustments. After training, the model is evaluated to provide insights into its performance.
Future Directions and Applications
PyReFT is not only a tool for current fine-tuning needs but also a platform for innovation. Researchers can experiment with:
- Custom Loss Functions: Adapt the fine-tuning process to optimize for specific downstream tasks.
- Dynamic Hyperparameter Adjustment: Implement techniques that adjust learning rates or batch sizes on the fly.
- Model-Agnostic Training Pipelines: Extend PyReFT to support an even wider range of models and tasks.
These possibilities make PyReFT an exciting development in the field of natural language processing and machine learning.
Conclusion
PyReFT represents a significant step forward in the realm of fine-tuning language models. Its reft-native design offers a flexible, modular, and efficient way to enhance the fine-tuning process, making it accessible to both researchers and practitioners. If you’re interested in experimenting with cutting-edge fine-tuning techniques, I encourage you to explore PyReFT further.
For a complete example of how to use the library, check out my GitHub repository where the full code is available. Happy fine-tuning!
Need Help with Your AI Project?
Whether you’re building a new AI solution or scaling an existing one, I can help. Book a free consultation to discuss your project.