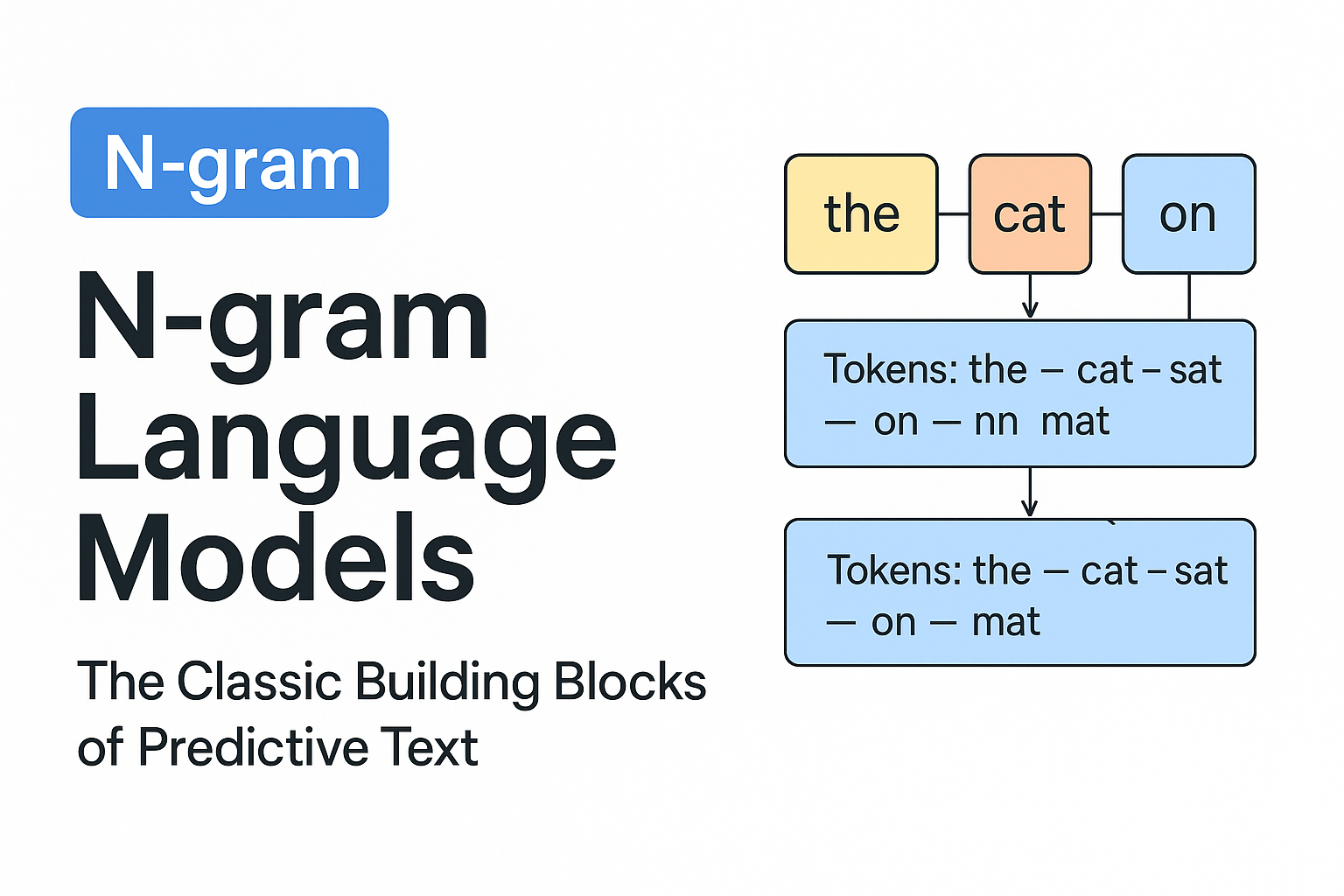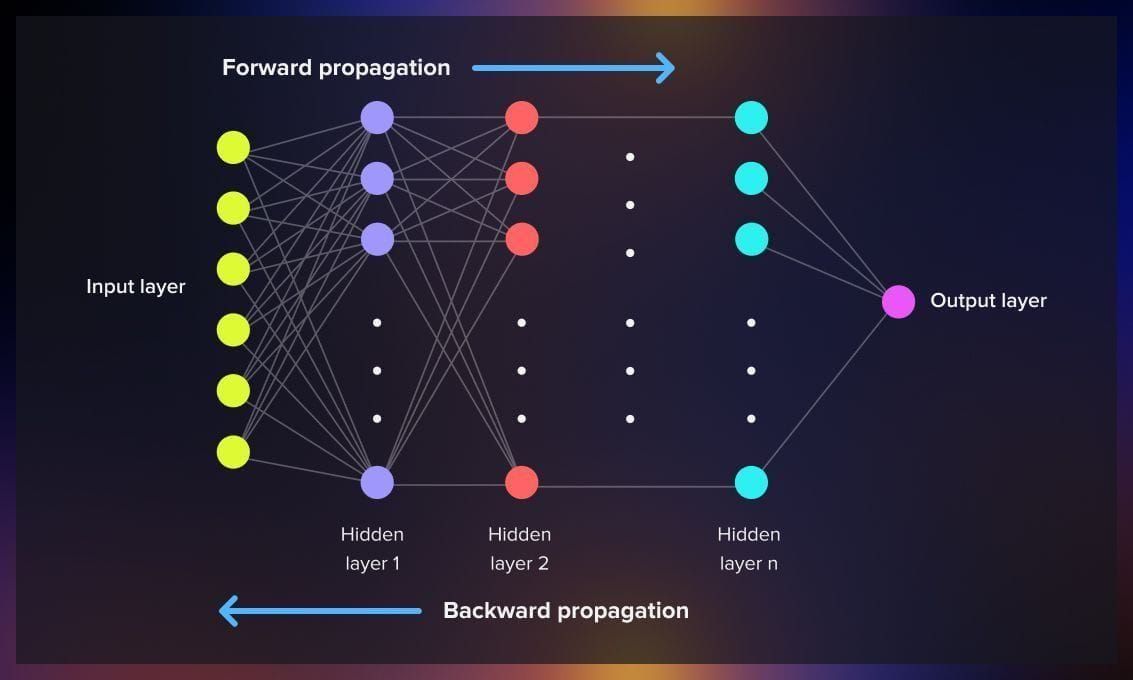
Yes, You Should Understand Backprop: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
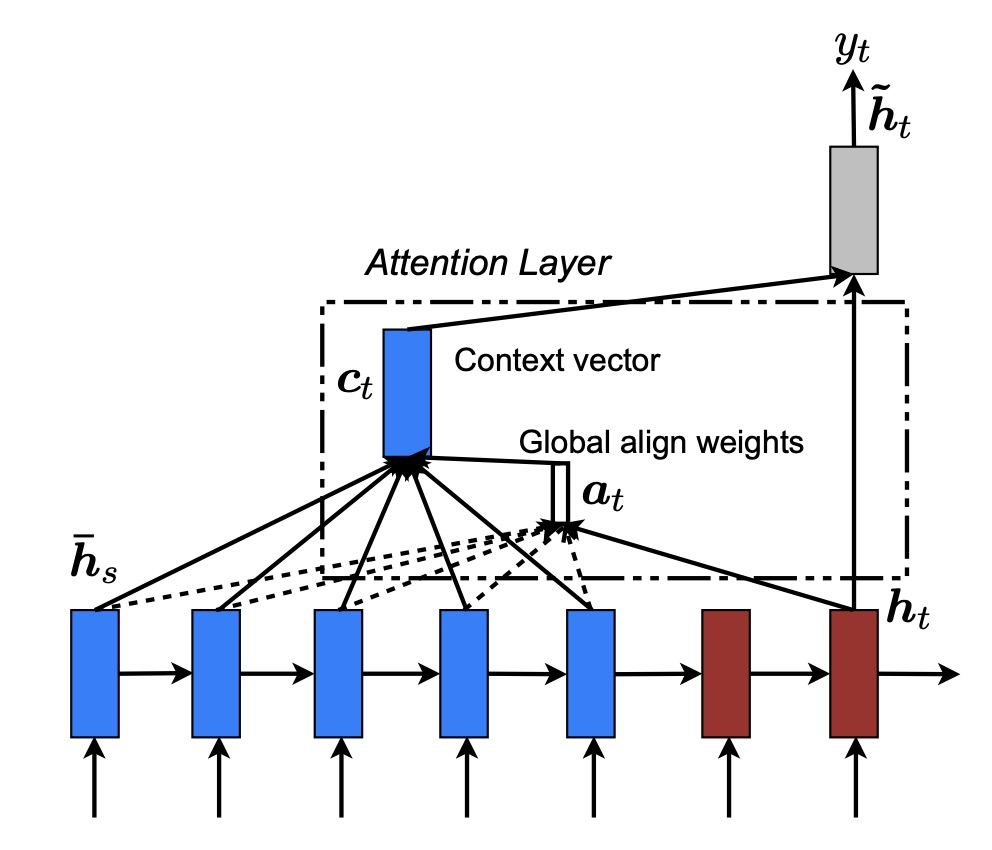
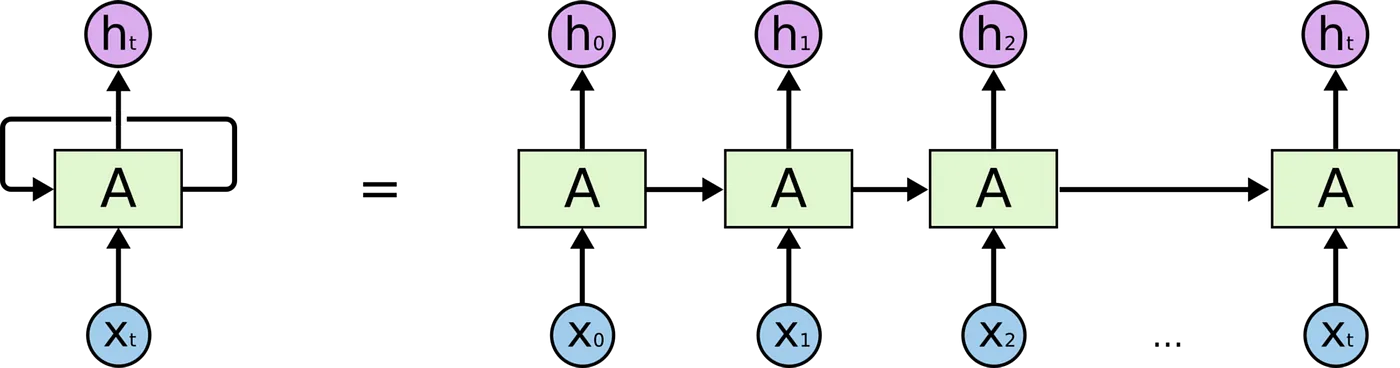
Backpropagation—originating in Linnainmaa’s 1970 reverse-mode AD thesis and popularized for neural nets by Rumelhart et al. in 1986—is the workhorse that makes deep learning feasible (en.wikipedi...